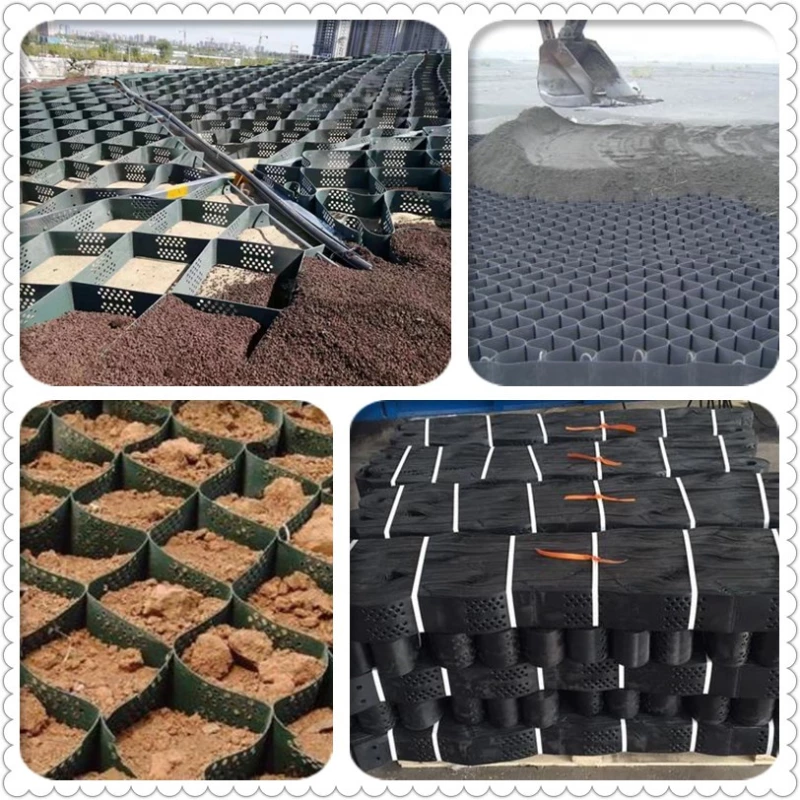
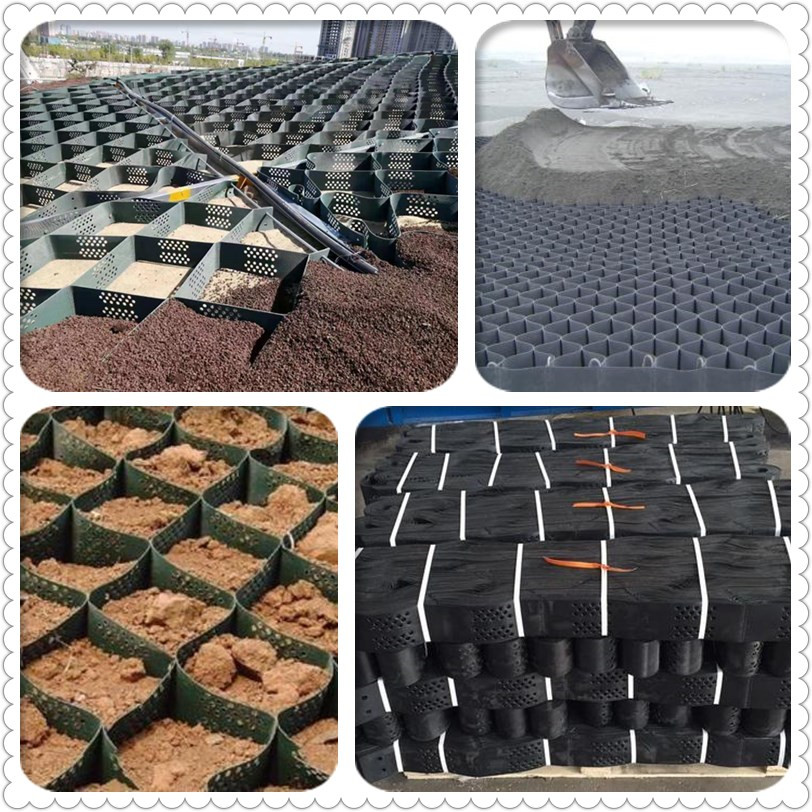
Geocell
It is a three-dimensional mesh cell structure formed by reinforced HDPE sheet material through high-strength welding. It is generally formed by ultrasonic needle welding. Due to engineering needs, some holes are punched in the diaphragm.

characteristic
1. It is flexible in expansion and contraction, and can be folded during transportation. It can be stretched into a net during construction, and filled with loose materials such as soil, gravel, concrete, etc., to form a structure with strong lateral restriction and large rigidity.
2. Light material, abrasion resistance, stable chemical performance, photooxidation resistance, acid and alkali resistance, suitable for different soils and deserts and other soil conditions.
3. High lateral restriction and anti-slip, anti-deformation, effectively enhance the bearing capacity of the roadbed and disperse the load.
4. Changing the geometric dimensions of geocell height, welding distance, etc. can meet different engineering needs.
5. Flexible expansion and contraction, small transportation volume; convenient connection and fast construction speed.
Fundamental
The reason why the geocell has its outstanding function and has attracted the attention of the engineering community, we should also start with its basic principles. When describing its principle in foreign literature, it is called "a honeycomb three-dimensional confinement system, which can significantly improve the performance of ordinary filling materials in load-bearing and pest control applications in a large range." Its key principle is three-dimensional confinement. . Everyone knows that when a car is driving on the desert, it will press two deep tracks, the pressed part sinks deeply, and the two sides of the track will bulge high. If the vehicle behind continues to advance along the rut, the sinking part will sink further, and the bulging part will bulge further, until the bulging part hits the chassis of the car, and the sinking rut buries most of the wheels, making it impossible to move forward. The reason for this is that when an external load acts on the surface of the foundation, according to Planttel theory and Taylor theory, it can be known that under the action of concentrated load, the active zone 1 sinks under pressure, and the force is decomposed and transmitted to both sides. The transition zone 2 and the transition zone 2 are passed to the passive zone 3, and the passive zone will deform and bulge without restriction.
Features:
1. It is flexible in expansion and contraction, and can be folded during transportation. It can be stretched into a net during construction, and filled with loose materials such as soil, gravel, concrete, etc., to form a structure with strong lateral restriction and large rigidity.
2. Light material, abrasion resistance, stable chemical performance, resistance to photooxidation, acid and alkali resistance, suitable for different soils and deserts and other soil conditions.
3. High lateral restriction and anti-skid, anti-deformation, effectively enhancing the bearing capacity of the roadbed and dispersing the load.
4. The geometric dimensions such as the height of the geocell and the welding distance can be changed to meet the needs of different projects.
5. Flexible expansion, small transportation volume, convenient connection and fast construction speed. That is to say, once the load acts on the subgrade, an active area with a taper shape will be formed under the load, which is squeezed through the transition area, so that the passive area will bulge. In other words, the bearing capacity of the foundation is determined by the shear force along the slip line and the force in the active, transitional and passive regions of movement. Not only can you clearly experience the true process of the above principles on sandy bases, but you will also find such a model on soft roads, but the rate of formation is slower than the change on sand. Even better roadbed materials still cannot avoid their lateral movement. The roadbed of general highways is several meters above the ground. It is not easy to absorb water and muddy, but long-term settlement still exists. Investigating the reasons, rainwater penetration, material loss, and base sinking are some of the reasons. Under the action of long-term rolling and vibration of the wheel load, the lateral displacement of the material to both sides of the subgrade section is undeniably another very important reason. . Take the highways at all levels in our province as an example, there is an "S"-shaped groove belt on the main carriageway of the road that can be clearly felt. Some expressways are no exception. The bumps of a car driving on the road are obviously stronger than the feeling of driving on an overtaking belt, especially at the road-bridge junction (commonly known as "bridge-head jumping"). This trench roadbed settlement is typical of the lateral slippage of roadbed materials.
サプライヤー連絡先
あなたにもっと多くのカテゴリーがあります。上で望むプロダクトを見つけることができないlfは、フォームを記入し、中国から輸入したいwhatproductsを教えてください。